Click to Skip Ahead
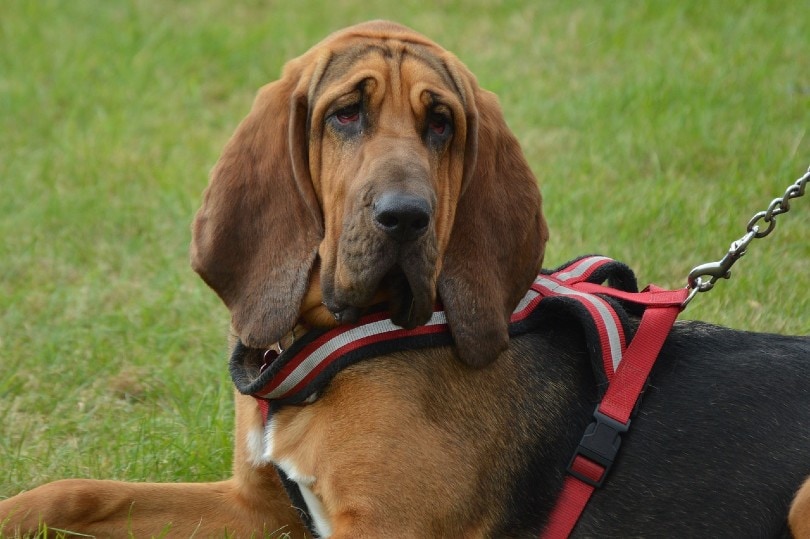
Few breeds can match the loyalty and gentleness of the Bloodhound. With their floppy ears and soulful eyes, the Bloodhound steals the hearts of those lucky enough to share their lives with them. The bond formed between a Bloodhound and their human is a treasure trove, and with proper care and dedication, this loving relationship could last over a decade. Let’s start with the good news: On average, Bloodhounds have a lifespan of 10–12 years.
Bloodhound Average Lifespan
The average 10-12 years will never be enough for a pet parent, but the Bloodhound’s lifespan is still respectable for a dog of this size. However, your Bloodhound’s lifetime will depend on their genetics, lifestyle, and care.

How to Care For Your Bloodhound for a Long Lifespan
Ensuring that your Bloodhound will live as long as possible starts with giving them the best care as soon as they enter your home. Unfortunately, there are things over which you have no control, but you can still try to do everything you can to help your dog develop in the best way.
1. Feeding & Diet
A diet with high-quality ingredients is paramount for any dog. Following your veterinarian’s recommendations is best, but here are some pointers. As a starting point, due to their size, Bloodhounds need a diet for large breeds and their stage of life (puppy, adult, or senior). Also, since Bloodhounds are large, deep-chested dogs, they can be affected by a life-threatening condition called gastric dilatation and volvulus1, or bloat.
Although the exact cause of this terrible disorder is unknown, you can limit the chances of it happening by feeding your dog several small meals a day and avoiding vigorous exercise immediately after eating. Using a slow-feeder bowl can prevent your dog from eating too quickly and swallowing air simultaneously, which is thought to increase the risk of a GDV.
2. Exercise
Bloodhounds are far from big, lazy dogs! They have an innate need for physical activity, and regular exercise is essential to prevent obesity, boredom, destructive behaviors, and all the other problems caused by the lack of physical stimulation.
Your Bloodhound will be happy to take long daily walks with you, which will keep their joints healthy. However, as they are exceptional tracking dogs with a keen sense of smell, you should keep them on a leash when walking in an unsecured area. You don’t want them wandering off after smelling a squirrel!
Bloodhounds are smart but stubborn and independent, especially when tracking a new scent, so they need a healthy dose of mental stimulation. Puzzle toys, obedience training, and scent games tap into their innate abilities and will keep them engaged.

3. Healthcare
There are two things that you can do to increase the likelihood of your Bloodhound living for as long a time as possible:
- Do careful research before buying your puppy. Since genetics can greatly influence your dog’s lifespan, it is essential to get your Bloodhound from a reputable breeder with ethical practices. These breeders use health and genetic disease screenings required by official breed associations. Good breeders should invite questions from prospective owners and ask several questions about how they plan to keep and care for their puppies. Don’t be disheartened if the breeder is quizzing you; be reassured!
- Always keep up with vet visits and health checkups. Regular checkups, annual vaccinations, and quick vet visits will help detect health problems.
- Gastric dilatation with or without volvulus (gas-filled stomach that may or may not twist)
- Bloat
- Hip and elbow dysplasia
- Heart disease
- Ear infections due to their long-hanging ears.
- Eye problems, entropion (rolling in of the eyelids), corneal ulceration
- Skin fold dermatitis
- Atopic dermatitis (allergies)
The American Bloodhound Club recommends checking that the following health tests have been done before buying a puppy from a reputable breeder:
- Hip and elbow evaluation
- Cardiac exam
The 3 Life Stages of a Bloodhound
Like any dog, the life stages of a Bloodhound can be broadly categorized into three main phases: puppyhood, adulthood, and senior years. Each stage brings unique challenges and joys, and understanding them will help you provide the best care and support for your Bloodhound throughout their life.
1. Puppyhood
Bloodhound pups have a lot of growing to do, so they are usually not considered adults until they are about 18 months old. A Bloodhound’s mental maturity might take even longer to arrive, which means your pup will quickly grow into a dog with an imposing stature while having the maturity of a rambunctious puppy!
Bloodhound puppies can be stubborn and may test your boundaries. You’ll need all your patience and training skills to keep your pup out of trouble during this time!
2. Adulthood
As your Bloodhound reaches adulthood, they become more stable and mature. They aren’t as fiery and mischievous as when they were young, but they still have a good amount of energy. This is usually the peak of their physical abilities and mental acuity. It is also during these years that you can enjoy their sweet and loyal nature and deepen your bond with them.
3. Senior Years
Around the age of 6 or 7, your Bloodhound will enter their senior years. Their bodies start to show signs of aging, and they experience a decrease in mobility and energy levels. Senior Bloodhounds will benefit from a modified diet and joint supplements, like glucosamine and chondroitin, to support their mobility.
Regular visits to the veterinarian to monitor their health become increasingly necessary as dogs age. Despite the natural slowing down, the Bloodhound’s love and loyalty remain steadfast, and they still appreciate spending quality time with their family.

How to Tell Your Bloodhound’s Age
Determining the age of a Bloodhound can be tricky, especially if you adopt or rescue one. However, a few physical and behavioral indicators can provide rough estimates of their age.
Teeth Condition
Checking the condition of a dog’s teeth can provide a few clues about their age. You may notice clean, white teeth with little to no wear in young Bloodhounds. As they age, their teeth might show signs of wear and tartar buildup, and there may even be missing teeth.
Graying
A Bloodhound’s coat can provide a few hints about their age. Young pups usually have smooth and shiny coats, while old dogs have coarse and dull ones. Graying around the muzzle and face is a common sign of aging in most breeds, but not all dogs will develop gray hair at the same rate.
Behavior
Young and not-so-small Bloodhounds are more excitable and require a bit more training and guidance to control their energy. Older dogs will generally be more stable, well-behaved, and have better obedience skills—though their stubbornness will never completely go away!

Conclusion
When choosing a dog, life expectancy is a crucial factor to consider. No pet parent wants to think about the inevitable, but that makes us cherish the times spent with our beloved pups even more. Therefore, although the lifespan of a Bloodhound may seem fleeting, every moment spent with these devoted companions is worth a lifetime of memories.
Featured Image Credit: markfizzwig, Pixabay